Product Choice
Introduction
The choice over whether a mesh of roof conductors, vertical air terminals, or fortuitous elements of the building etc are used, is dependent on the Lightning Protection Designer and the nature of the structure itself. There is no such thing as a standard Lightning Protection Kit/ Lightning Protection System. Each building needs to be examined in its own right and a system designed to suit that particular structure and its use or purpose.
The type of conductor used – aluminium, copper, composite or PVC covered – has a bearing on which fittings to use, as does the shape and size of the conductor. Conductors can be supplied in a rectangular and solid circular section.
Air Terminals/Masts
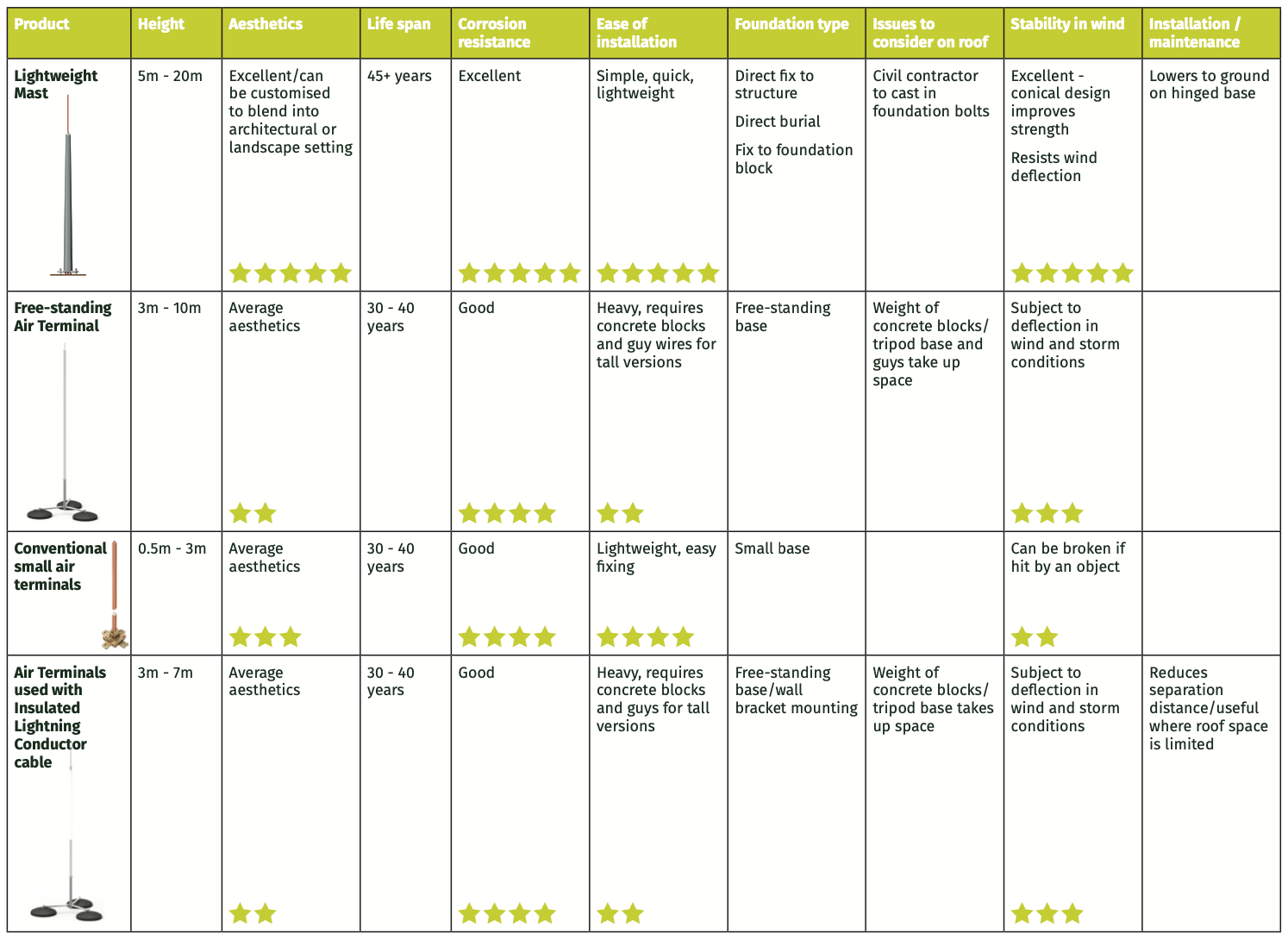
Kingsmill offer a comprehensive range Lightning Protection Air Terminals and Lightning Interception Masts:
- Lightweight Lightning Mast (5m to 20m in height)
- Free-standing Air Terminals (1m to 10m in height)
- Conventional Small Air Terminals (0.5m to 3m in height)
- Air terminals for use with Insulated Lightning Conductor cable (3m to 7m in height)
This give the architect, designer, contractor and client flexibility over height, as well as installed aesthetics of the system.
Each system has its features and benefits which are summarised below:
From BS:EN 62305 . . .
The Lightning Protection Designer may need to consider the following when designing a system . . .
Roof mesh conductor system
BS:EN 62305 recommends the use of a protective mesh of conductors laid over the structure to be protected. This mesh can be supplemented with the use of Air Terminals. The risk assessment carried out from BS:EN 62305-2 determines both the Lightning Protection Level (LPL) and Lightning Protection System (LPS) for a structure.
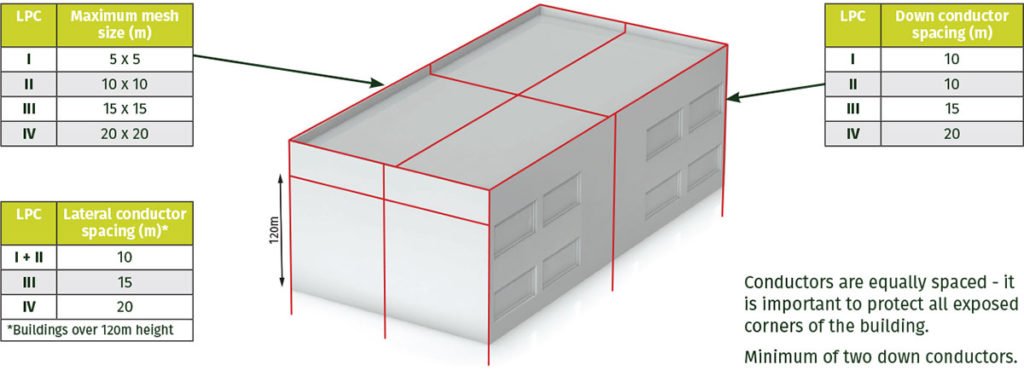
Roof mesh spacing
The roof mesh is spaced in accordance with guidelines contained within BS:EN 62305-3. This can be summarised below:
Example of a roof mesh system
Perimeter conductors should be placed close to the edge of the structure. If possible, place down conductors at each corner as well as spacing them equally around the structure.
A minimum of two down conductors is required, whether an Air Terminal, Mesh or Rolling Sphere concept is used.
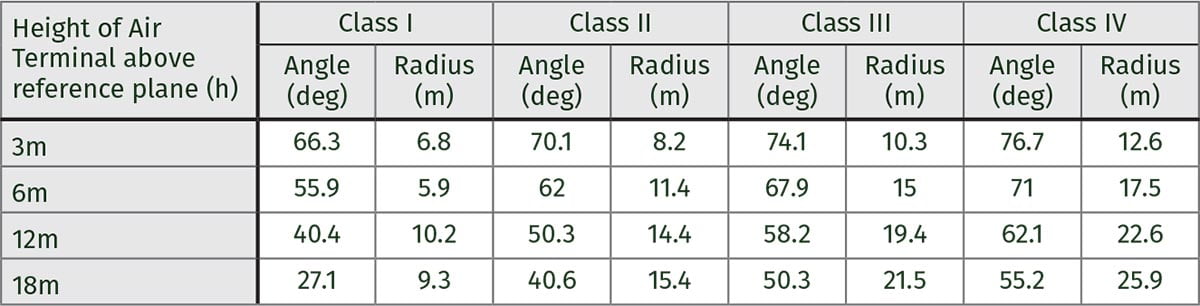
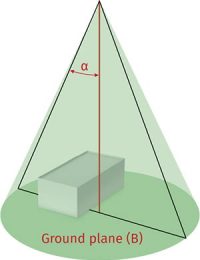
Protective angle/zone of protection
The protective angle differs according to the class of Lightning Protection System (ie I, II, III or IV) and the height of the Air Terminal above the reference plane.
Examples of how the protective angle changes with height and LPS class are shown below.
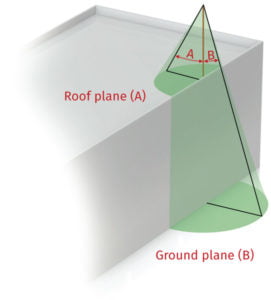
Roof mounted terminal
In this circumstance there are two reference planes and angles:
A Roof to tip of Air Terminal
B Ground to tip of Air Terminal
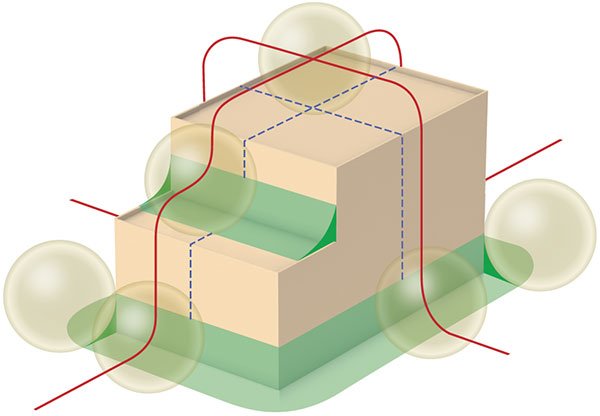
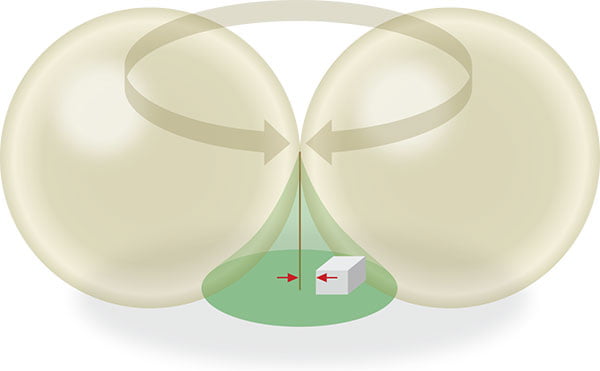
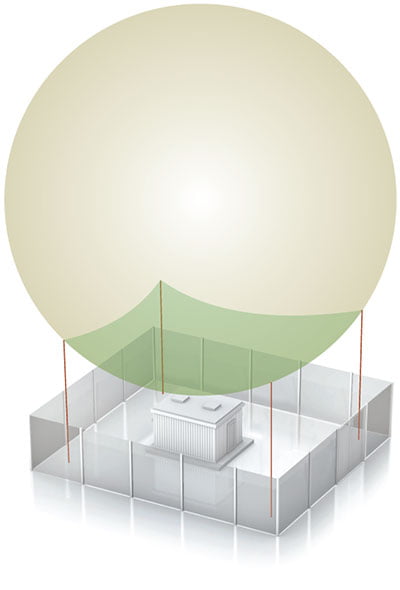
Rolling Sphere
The Rolling Sphere can also be used to determine protective area.
Some examples of Rolling Sphere applications . . .
The sphere is rolled all over the structure. Where the sphere touches the building, protection is required.
This protection is usually in the form of a mesh system of conductors.
Buildings over 60m in height should have both lateral (side) and roof conductors installed.
Spacing of The Lightning Protection conductors would still conform to the roof mesh conductor system tables (above).